Range of Motion
What is Range of Motion?
Range of motion (ROM) is the measurement of the amount of movement around a specific joint or body part. It is commonly measured during an occupational therapy evaluation. Other impairments that your therapist may measure include strength, gait, flexibility, or balance.
Measured Motions
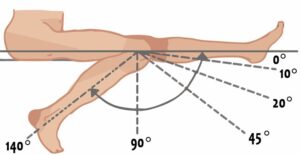
Passive Range of Motion occurs mostly around a joint if you are not using your muscles to move. Someone else must manually move your body while you relax. A machine may also be used to provide passive ROM. For example, after knee replacement surgery, you may not be able to use your muscles to move the knee. Your therapist may straighten and bend your knee for you, passively moving your leg. A device called continuous passive motion (CPM) can also be used to provide passive ROM.
Active-Assistive Range of Motion occurs when you are able to move your injured body part, but you may require some help to move to ensure further injury or damage does not occur. The assistance that helps move your body can come from you or another person. It may also come from a machine or mechanical device.
Active Range of Motion occurs when you use your muscles to help move your body parts. This requires no device or other person to help you move. This is a “strictly you” motion. Active ROM is used when you are able to start moving independently after an injury or surgery. Strengthening exercises are a form of active ROM.
User Reviews
Jennifer Nuzzo
a year agoKelly is great! I had an ongoing issue with my shoulder and after a few sessions I felt good as new! Kelly is very intuitive. She always figures out just what my body needs. I wouldn't hesitate to book a session with her. Your body will thank you.
Rating: 5 / 5
Cyndy Landry
2 years agoI have never been to a health and wellness, or doctors office that can make me feel like a completely different person! After being seen by Kelly I can take on my day and week with clarity and pain free. It’s amazing and I highly recommend for everyone, even without pains, to get cranial therapy!
Rating: 5 / 5
Ella Grace
2 years agoKelly is incredible! I have been seeing her for a few years and she is always so kind, super knowledgeable, and wonderfully skilled.
Rating: 5 / 5
Jeffrey Purtell
in the last weekI've been receiving craniosacral therapy from Kelly for the last few months. Her knowledge, compassion and intuition are priceless!
Rating: 5 / 5
Roberta Cordeau
in the last weekI have been seeing Kelly for craniosacral therapy for 6+ months now and it has been life changing for me. Over the years, I have tried so many different methods to try and manage my very sensitive nervous system and so far cranio has been the only practice I have found that helps me regulate and feel better. Kelly also helps me with my physical ailments due to my hypermobility. She is a gifted healer!
Rating: 5 / 5
Kendra Beveridge
in the last weekKelly is amazing at what she does. Each time I have cranial sacral done, I feel like I can deal with my week with a whole new perspective! Thank you, Kelly!
Rating: 5 / 5
John Tierney
in the last weekKelly is great. She has helped me so much with my problem I highly recommend her.
Rating: 5 / 5
Give the Gift of Healing
Looking for the perfect gift? A Therapeutic Healing Gift Card is a thoughtful way to show you care. Treat your loved ones to relaxation and rejuvenation, tailored to their needs.
Personalized Care
Let them choose the therapy or treatment that best suits their needs.
Stress Relief
Help your loved ones unwind and find balance in their lives.
Perfect for Any Occasion
A great gift for birthdays, anniversaries, or just because.
